The process begins by containerizing the Django application with a Dockerfile and installing production-ready packages such as django-environ for secure environment variables, gunicorn as the WSGI server, psycopg2-binary as the PostgreSQL adapter, and whitenoise for static file management. The Docker image is tested locally and then pushed to GHCR.
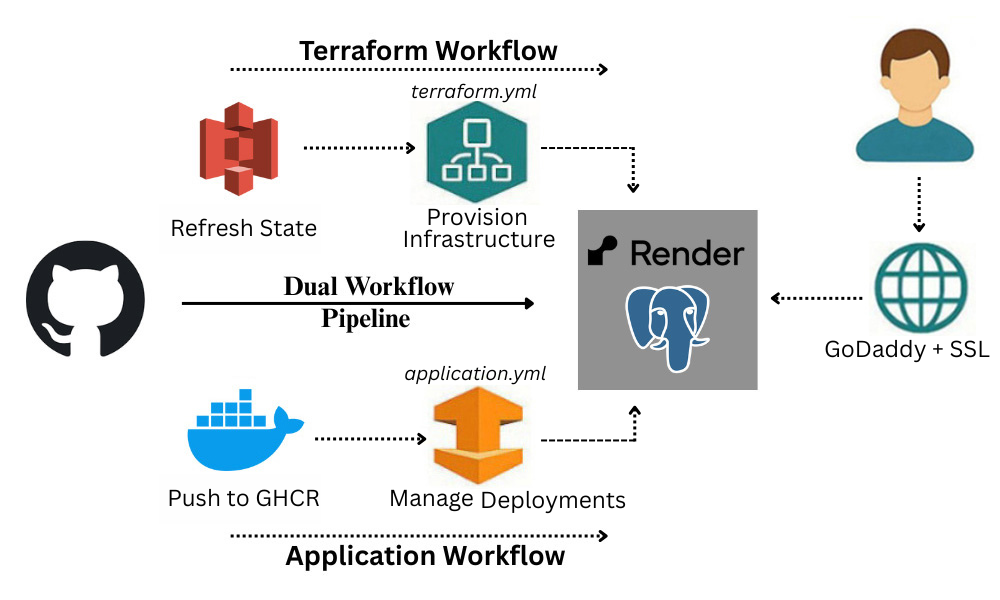
Terraform scripts (main.tf) define the Render web service and PostgreSQL database. Terraform state files are stored in S3, allowing the workflow to compare existing infrastructure state with the updated configuration before applying changes. A Render deployment hook is configured to trigger redeployments automatically when a new Docker image reference is pushed.
The CI/CD pipeline operates through two workflows. The Terraform workflow runs via terraform.yml GitHub Action to provision or update infrastructure, handling state files from S3 to ensure safe and idempotent changes. The Application workflow runs via application.yml GitHub Action to build Docker images, push to GHCR, and trigger the Render deployment hook for redeployment. These workflows are linked so that infrastructure changes are applied before application deployments, maintaining order and reliability. The pipeline automates environment variable configuration for both the Render service and the Django application, minimizing manual intervention.
This architecture demonstrates modern Infrastructure as Code principles combined with containerized deployments on Render, providing a robust, reproducible, and automated pipeline for Django applications. By integrating Terraform and deployment hooks, the system enables fully automated provisioning and deployment, streamlining DevOps practices without the need for AWS services.